The LDP RLFA configuration process can be divided into the following tasks:
|
1.
|
Enable label-switching on the interface on NSM. |
|
2.
|
Establish ISIS routing between the nodes (to distribute reachability information within the MPLS cloud) |
|
3.
|
Configure ISIS RLFA on Source node |
|
4.
|
Enabling LDP on an interface in the LDP daemon |
|
5.
|
Configure LDP FRR with Auto-targeted-session (Allow creating TLDP session dynamically) |
|
6.
|
Enable BFD interval globally and for all ISIS enabled interfaces |
|
•
|
Faster convergence can be achieved with lower BFD interval enabled globally. |
|
•
|
Dynamically created RLFA T-LDP sessions will be removed only after disabling LDP auto-targeted-session CLI or LDP FRR. |
|
•
|
When targeted-peer ipv4 CLI is configured with auto-targeted-session CLI, T-LDP session created for targeted-peer only remove after disabling auto-targeted-session CLI. |
|
•
|
After Enabling ISIS RLFA, Both LFA and RLFA computation will be done and RLFA path will be preferred to provide node-protection. |
|
•
|
Better convergence can be achieved with LDP-IGP-SYNC enabled. |
Assumptions and Limitations
|
•
|
RLFA Backup path computation will be supported only via IGP as IS-IS. |
|
•
|
Only LDP(MPLS) will be used as a tunnel mechanism to reach a Remote-LFA repair node. |
|
•
|
Only IPv4 protocol is supported. |
|
•
|
RFC 7916 [LFA-MANAGE] is not supported. |
|
•
|
ECMP will not be supported for RLFA next-hop. |
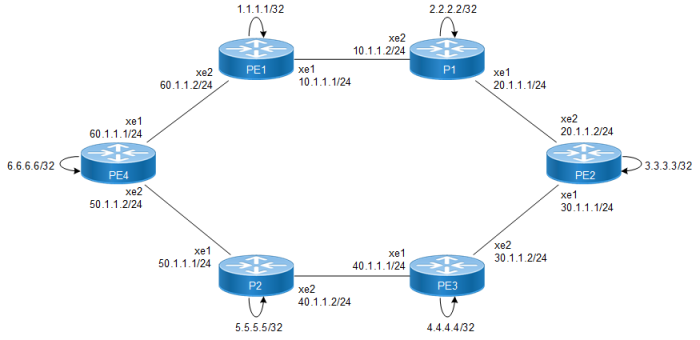
Topology
The below topology shows the configuration required to enable the RLFA feature.
Figure 79. RLFA Topology