Proxy ARP and Local Proxy ARP
Overview
Proxy ARP (RFC 1027) is a technique by which a device on a given network answers the ARP queries for a network address that is not on that network. The Proxy ARP is aware of the location of the traffic's destination, and offers its own MAC address as destination. The captured traffic is then typically routed by the Proxy to the intended destination via another interface. Proxy ARP can help machines on a subnet reach remote subnets without the need to configure routing or a default gateway.
Use no ip proxy-arp to disable Proxy ARP, Proxy ARP is disabled by default.
Topology
Figure 79. Sample topology
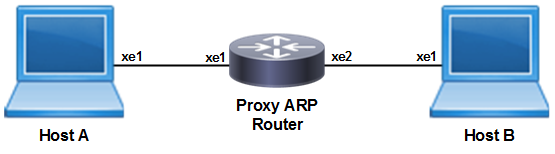
Host A
|
#configure terminal |
Enter Configure mode. |
|
(config)#interface xe1 |
Specify the interface to be configured on Host A |
|
(config-if)#ip address 20.20.0.3/24 |
Configure the ip address on the interface |
|
(config)#commit
|
Commit the candidate configuration to the running configuration |
|
(config)#end |
Exit interface and configure mode |
Host B
|
#configure terminal |
Enter Configure mode |
|
(config)#interface xe1 |
Specify the interface to be configured on Host B |
|
(config-if)#ip address 20.20.1.2/24 |
Configure the ip address on the interface |
|
(config)#commit
|
Commit the candidate configuration to the running configuration |
|
(config)#end |
Exit interface and configure mode |
Enable Proxy ARP
|
#configure terminal |
Enter Configure mode. |
|
(config)#interface xe1 |
Specify the interface connected to Host A |
|
(config-if)#ip address 20.20.0.1/24 |
Configure the ip address on the interface |
|
(config-if)#interface xe2 |
Specify the interface connected to Host B |
|
(config-if)#ip address 20.20.1.1/24 |
Configure the ip address on the interface |
|
(config-if)#interface xe1 |
Specify the interface to configure Proxy ARP |
|
(config-if)#ip proxy-arp |
Enable Proxy ARP |
|
(config)#commit
|
Commit the candidate configuration to the running configuration |
|
(config)#end |
Exit interface and configure mode |
Validation
#show running-config arp
!
interface xe1
ip proxy-arp
! The show arp command on the hosts shows the ARP table entries to reach different subnets. Ping Host A from Host B. The ARP table should have the router’s xe1 interface MAC address to reach Host A. Execute the below command at Host B:
#show arp
Flags: D - Static Adjacencies attached to down interface
IP ARP Table for context default
Total number of entries: 2
Address Age MAC Address Interface State
20.20.0.3 00:02:39 ecf4.bbc0.3d71 xe1 STALE.