LDP Remote Loop-Free Alternate (RLFA)
A basic mechanism using Loop-Free Alternates (LFAs) is described in RFC5286 that provides good repair coverage in many topologies, especially those that are highly meshed.
However, some topologies, notably ring-based topologies, are not well protected by LFAs alone. This is because there is no neighbor of the Point of Local Repair (PLR) that has a cost to the destination via a path that does not traverse the failure that is cheaper than the cost to the destination via the failure.
RFC 7490 provides extensions to the basic repair mechanism in which tunnels are used to provide additional logical links that can be used as loop-free alternates where none exist in the original topology. It provides loop-free alternates that guarantee only link protection.
RFC 8102 provides remote-loop-free-based IP fast reroute mechanisms that specifies procedures for determining whether or not a given PQ-node provides node protection for a specific destination. It provides node protection for all destinations covered by the same remote-LFA alternate, in case of failure of the primary next-hop node
ISIS shall compute PQ node and LDP shall dynamically create tunnel to PQ node so that if primary path fails traffic can be rerouted to backup rLFA tunnel and hence to destination.
Remote LFA involves the use of a tunnel to a next-hop that is not directly connected. This is the primary difference between the LFA and Remote LFA.
RLFA Terminology
Terms used for defining tunnel as below:
Repair tunnel
A tunnel established for the purpose of providing a virtual neighbor that is a Loop-Free Alternate.
P-space
The P-space of a router with respect to a protected link is the set of routers reachable from that specific router using the pre-convergence shortest paths, without any of those paths (including equal cost path splits) transiting that protected link.
For example, the P-space of S with respect to link S-E is the set of routers that S can reach without using the protected link S-E.
Extended P-space
Consider the set of neighbors of a router protecting a link. Exclude the router reachable over the protected link from that set of routers. The extended P-space of the protecting router with respect to the protected link is the union of the P spaces of the neighbors in that set of neighbors with respect to the protected link.
Q-space
Q-space of a router with respect to a protected link is the set of routers from which that specific router that can be reached without any path (including ECMP Splits) transiting that protected link.
PQ node
A PQ node of a node S with respect to a protected link S-E is a node that is a member of both the P-space (or the extended P-space) of S with respect to that protected link S-E and the Q-space of E with respect to that protected link S-E. A repair tunnel endpoint is chosen from the set of PQ-nodes.
Remote LFA (RLFA)
The use of a PQ node rather than a neighbor of the repairing node as the next hop in an LFA repair.
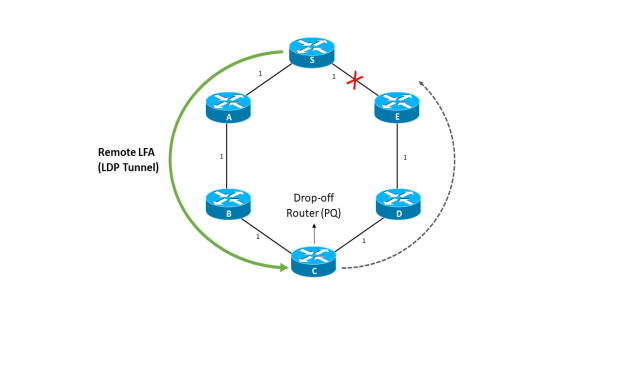
In Figure 78, S can reach A, B, and C without going via S-E; these form S's extended P-space with respect to S-E. The routers that can reach E without going through S-E will be in E's Q-space with respect to link S-E; these are D and C.B has equal-cost paths to E via B-A-S-E and B-C-D-E, and so the forwarder at S might choose to send a packet to E via link S-E. Hence, B is not in the Q-space of E with respect to link S-E. The single node in both S's extended P-space and E's Q-space is C; thus, node C is selected as the repair tunnel's endpoint. Thus, if a tunnel is provided between S and C as shown in Figure 79. RLFA Topology, then C, now being a direct neighbor of S, would become an LFA for D and E.
Establishing RLFA Tunnel
To calculate the Remote LFA backup path and to determines the Remote LFA node the software requirement can be broadly classified as below:
IS-IS
ISIS shall calculate Repair path that are P space (routers it can reach without traversing the protected link) and Q space (routers that can reach the protected destination without traversing the protected link). Hence routers that belong to both spaces called as PQ routers has to be calculated. It has to inform LDP about PQ node so that RLFA tunnel can be established.
LDP
LDP shall establish targeted session with PQ node and shall advertise label to peer node for the destination FEC. LDP shall send primary and backup path FTN/ILM add/delete info to NSM for further programing.
NSM
NSM shall maintain Primary and Backup path FTN/ILM and shall send information to HSL for data-plane programing.
HSL
HSL program primary and backup FTN/ILM entry in hardware.